[주간 강좌] 병행 시뮬레이션(Co-Simulation)
내용
1. 병행 시뮬레이션(Co-Simulation)의 필요성
- 추상화 수준(abstraction level)의 혼재
- 언어의 차이
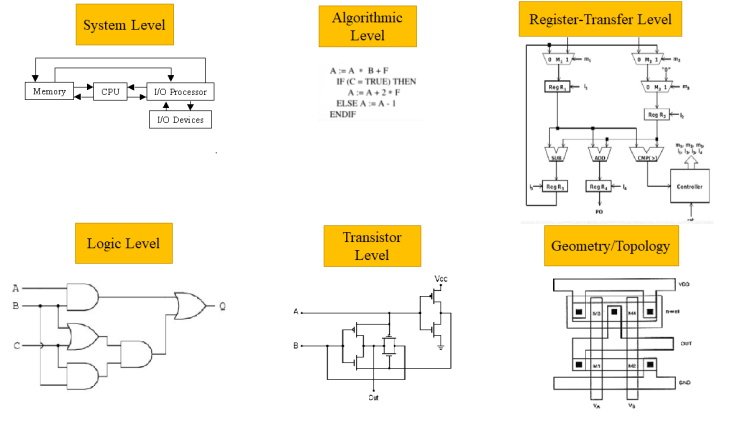
- 구체성의 차이 - Gajski-Kuhn Y-chart [그림출처: 1 , 2]
3-Domains: Behavioral / Structural / Physical - Concerns in each abstraction level
- Architecture: IP availability, Needs on the market
- Functionality & Algorithm
- Number of Clocks & Data-path bit-width
- Clock skew & violation
- Die size & Power consumption
- Clock & Thermal distribution
- Test automation
- Design Flow
Lowering Abstraction Level
2. 추상화 수준이 혼재될 수 밖에 없는 이유
- Design Under Test: Register-Transfer Level
- Test Environment: Transaction Level
- 실제와 근접한 테스트 입력
- 방대한 테스트 입출력 및 검사
- 완성되지 않은 DUT
- 테스트 환경 구축
- HDL 모델을 시험하는 3가지 방법
- 대화창 명령
- HDL 테스트 벤치
- 상위수준 언어사용 - SystemC/C++ 로 하드웨어 기술 예
- 도구 사용법
- QuestaSim 사용법
- VisualStudio C++ 에서 SystemC 모델 컴파일 옵션
4. 예제: 이미지 처리 RTL 모델 [예제 다운로드]
- 시뮬레이터의 속도
- 트랜잭션 수준 테스트
- 가속기 / 에뮬레이터
- FPGA Proto-Typing
5. 예제: Apple ][ [예제 다운로드]
- CPU 6502 in Verilog (Synthesizable RTL)
- Memory model in SystemC/C++
- Testbench in SystemC/C++
- Screen App. in C++ with SDL2 multimedia library
- PIPE (Inter-Process Communication) between SystemC & Screen App.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
6. 결론
- Verilog
- 모양이 다른 컴퓨팅 언어 중 하나 - SystemC/C++
- 시스템 수준 모델링 도구 - 추상화 수준이 혼재된 SoC 설계에서 병행 시뮬레이션(co-simulation)은 필수
-----------------------------------------------------------------
[참고]
- AI Can't Design Chips Without People, EETimes [Link]
- SystemC Quick Reference Card [Link]
- Verilog Quick Reference Card [Link]
- Verilog Quick Reference Guide(2001) [Link]
-------------------------------------------------------------------
예제1:
Module boundary:
Verilog:
module SR_ff_Behavioral(s,r,clk,reset,q,q_bar);input s,r,clk,reset;output q,q_bar;......endmodule
SystemC(C++)
class SR_ff_Behavioral : public sc_foreign_module{public:sc_in<bool> clk;sc_in<sc_logic> s, r, reset;sc_out<sc_logic> q, q_bar;SR_ff_Behavioral(sc_module_name nm) // Constructor: sc_foreign_module(nm, "SR_ff_Behavioral"),{}~SR_ff_Behavioral(){}};
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Verilog: Event sensitize
// Verilogalways @(posedge clk) // Clock's edgebegin......end
SystemC(C++): Even & Call-Back
// SystemCSC_MODULE(SR_ff){......SC_CTOR(SR_ff): // Constructor{SC_METHOD(SR_ff_Method);sensitive << clk;}};
Member function,
void SR_ff:: SR_ff_Method (){if (clk.read()){......}}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Binding signals
Verilog:
wire s1, r1, q1, q1_bar;SR_ff_Behavioral U1(.clk(clk),.reset(reset),.s(s1),.r(r1),.q(q1),.q_bar(q1_bar) );
SystemC(C++):
sc_signal<sc_logic> s1, r1;sc_signal<sc_logic> q1, q1_bar;SR_ff* U1_SR_ff;SC_CTOR(sc_SR_ff_TB) : ... // Constructor{U1_SR_ff = new SR_ff("U1_SR_ff");U1_SR_ff->clk(clk);U1_SR_ff->reset(reset);U1_SR_ff->s(s1);U1_SR_ff->r(r1);U1_SR_ff->q(q1);U1_SR_ff->q_bar(q1_bar);}
------------------------------------------------------------
Behavior description
Verilog:
always @(posedge clk) // Clock's edgebeginif (reset) // Synchronous resetbeginq = 1'b0;q_bar = 1'b1;endelsebegincase({s,r}) // Truth-Table{1'b0,1'b0}: begin q = q; q_bar = q_bar; end{1'b0,1'b1}: begin q = 1'b0; q_bar = 1'b1; end{1'b1,1'b0}: begin q = 1'b1; q_bar = 1'b0; end{1'b1,1'b1}: begin q = 1'bx; q_bar = 1'bx; endendcaseend // if~elseend // always()
SystemC(C++)
void SR_ff:: SR_ff_Method (){if (clk.read()){if (reset.read() == sc_logic('1')){q.write(sc_logic('0'));q_bar.write(sc_logic('0'));}else{sc_lv<2> sr;sr = ((sc_lv<1>)s.read(), (sc_lv<1>)r.read());switch ((sc_uint<2>)sr) // Truth-Table{case 0: // s=0, r=0// DO NOTHING// q & q_bar: Keep previous valuesbreak;case 1: // s=0, r=1q.write(sc_logic('0'));q_bar.write(sc_logic('1'));break;case 2: // s=1, r=0q.write(sc_logic('1'));q_bar.write(sc_logic('0'));break;case 3: // s=1, r=1q.write(sc_logic('x'));q_bar.write(sc_logic('x'));break;}}}}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Blocking & Non-Blocking Assign
Co-Simulation Result
===========================================
예제2:
==============================================
예제3: Apple ][









댓글 없음:
댓글 쓰기